Effective financial management is crucial for an agricultural cooperative to ensure financial stability, allocate resources efficiently, manage risks, enhance profitability and sustainability, maintain transparency, and support informed decision-making.
Therefore, through partnership between Chamroeun Microfinance PLC and CamboDHRRA under the SSNUP program (Smallholder Safety Net Upscaling Program), from November 2021 to July 2023, CamboDHRRA provided capacity building on business planning to 30 agricultural cooperatives in Kampot, Kampong Speu, Kampong Chhnang, Battambong, Siem Reap, Utdor Meanchey, Preah Vihea, Steung treng, Kampong Thom and Prey Veng provinces. Each agricultural cooperative received two-day training. In total, there are 197 board of directors, internal control committees and personnels included 96 women and 36 youth were capacitated. The financial management training can greatly benefit the board of directors of an agricultural cooperative in understanding financial statements, budgeting and planning, financial risk management, investment evaluation, financial governance and compliance, effective decision-making, and stakeholder communication.
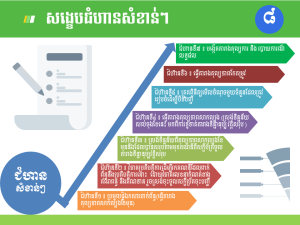
It’s noted that effective financial management is important for an agricultural cooperative as followings:
• Financial stability: Effective financial management helps ensure the stability and sustainability of the agricultural cooperative. It involves budgeting, forecasting, and managing cash flows to ensure that the cooperative has sufficient funds to cover its expenses, invest in growth and development, and withstand any financial setbacks.
• Capital management: Financial management helps in managing the cooperative’s capital effectively. It involves assessing the capital needs of the cooperative, identifying potential sources of funding, and making informed decisions about borrowing, equity investments, or grants to support the cooperative’s operations and expansion plans.
• Resource allocation: Financial management allows for efficient allocation of resources within the agricultural cooperative. It involves prioritizing and distributing available funds to various activities, such as purchasing necessary equipment, investing in research and development, or implementing marketing strategies. By managing resources effectively, the cooperative can optimize its productivity and profitability.
• Risk management: Financial management helps identify and manage financial risks associated with the agricultural cooperative. It involves analyzing potential risks, such as fluctuating commodity prices, natural disasters, or changes in government policies, and developing appropriate risk mitigation strategies, such as hedging, insurance, or diversification. By managing risks, the cooperative can safeguard its financial stability and protect its members’ investments.
• Financial reporting and transparency: Financial management ensures accurate and transparent financial reporting within the agricultural cooperative. It involves maintaining proper accounting records, preparing financial statements, and complying with regulatory requirements. Transparent financial reporting builds trust among members, stakeholders, and lenders, and enhances the cooperative’s credibility and reputation.
• Profitability and sustainability: Financial management helps improve the profitability and long-term sustainability of the agricultural cooperative. It involves analyzing costs, revenues, and profitability margins to identify areas for improvement. By implementing cost-saving measures, diversifying income sources, or adopting sustainable farming practices, the cooperative can enhance its financial performance and resilience.
• Decision-making support: Financial management provides valuable information and analysis for informed decision-making within the agricultural cooperative. It involves conducting financial feasibility studies, evaluating investment opportunities, and assessing the economic viability of various projects or initiatives. By making sound financial decisions, the cooperative can achieve its strategic objectives and meet the needs of its members effectively.


 Cambodhrra Cambodian Partnership for Development Human Resource in Rural Area Association
Cambodhrra Cambodian Partnership for Development Human Resource in Rural Area Association